Providing In-Home Care for Diabetic Patients
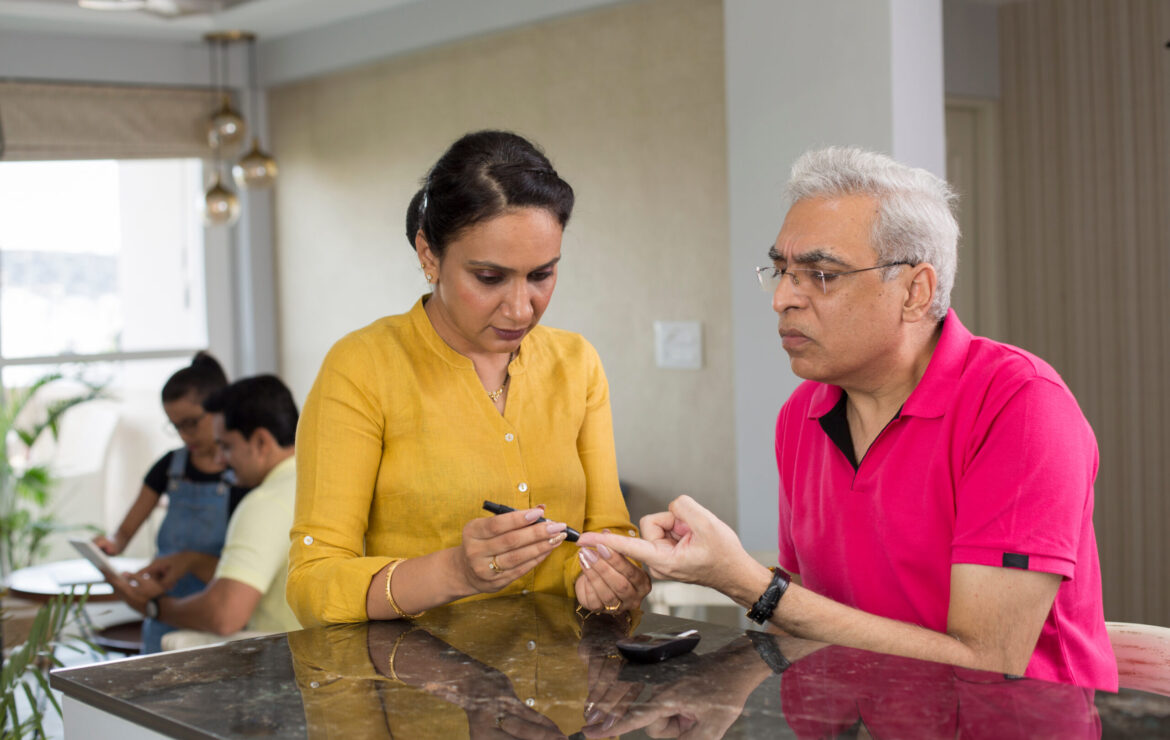

Caring for someone with diabetes involves a multifaceted approach that includes monitoring their blood sugar levels, managing their diet, ensuring they get regular exercise, providing mental health support, and possibly administering medications or insulin.
Understanding Diabetes
First, it’s crucial to understand the type of diabetes of your patient(s) for effective management and treatment during in-home care. There are mainly two types: Type 1 diabetes, where the body does not produce insulin, and Type 2 diabetes, where the body does not use insulin properly.
Here is a brief summary of the differences between Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes:
Type 1 Diabetes:
- Cause: Autoimmune destruction of insulin-producing cells.
- Onset: Typically in children and young adults, sudden onset.
- Insulin Production: Little to no insulin produced.
- Risk Factors: Genetic predisposition, family history, certain infections.
- Symptoms: Frequent urination, extreme thirst, weight loss, fatigue, blurred vision.
- Treatment: Daily insulin injections or pump, blood sugar monitoring, balanced diet, regular exercise.
Type 2 Diabetes:
- Cause: Insulin resistance and eventual insulin deficiency, often related to lifestyle factors.
- Onset: Typically in adults over 45, but increasingly in younger people, gradual onset.
- Insulin Production: Body produces insulin but cannot use it effectively.
- Risk Factors: Obesity, sedentary lifestyle, family history, age, certain ethnicities, high blood pressure, abnormal cholesterol levels.
- Symptoms: Increased thirst, frequent urination, hunger, fatigue, blurred vision, slow-healing sores.
- Treatment: Lifestyle changes, oral medications, sometimes insulin, blood sugar monitoring, weight management.
Key Differences:
- Cause: Type 1 is autoimmune; Type 2 is related to insulin resistance and lifestyle.
- Onset: Type 1 in younger individuals, sudden; Type 2 in adults, gradual.
- Insulin: Type 1 requires insulin; Type 2 may initially be managed with lifestyle changes and medications.
Important Daily Tasks
1. Maintaining normal blood sugar levels is crucial so regular blood sugar monitoring helps in managing the condition effectively. Use a glucometer to check blood sugar levels regularly. The frequency depends on the doctor’s advice. Keeping a log of the readings can help identify patterns and triggers affecting blood sugar levels.
2. Having a balanced diet that includes a balance of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. Planning meal times and focusing on high-fiber foods, whole grains, fruits, and vegetables helps maintain optimal glucose levels. Learning to count carbs, as they have the most impact on blood sugar levels, and ensuring they have regular meals and snacks to avoid blood sugar spikes and dips.
3. Encourage regular physical activity, which helps manage blood sugar levels and overall health. Tailor the exercise plan according to the ability and preference of your patient. Monitor how different activities affect blood sugar levels, as exercise can lower them.
4. Always be prepared for the unexpected. Keep a diabetes emergency kit handy, which includes glucose tablets, snacks, and medical information, including patient ID. Having glucose tablets, a snack and water to help stabilize blood sugar levels if there is an unexpected drop in blood sugar. Have an action plan for managing severe hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia
5. Medication adherence is key. Ensure they take their medications as prescribed (This may include oral medications or insulin injections).If they need insulin, learn how to administer it correctly. Be aware of different types of insulin and their action times.
6. Keeping regular medical check-ups is an essential part of managing diabetes. Work closely with their healthcare team, including doctors, dietitians, and diabetes educators. Ensure regular check-ups and tests like HbA1c, cholesterol levels, and kidney function. Try to schedule check-ups at least once a year or as your healthcare provider recommends to ensure your diabetes management plan is as effective and up-to-date.
7. Stay informed about diabetes management by attending diabetes education programs if available. Managing diabetes can be stressful and stress can have a significant effect on blood sugar levels. Providing emotional support and introducing stress-reduction techniques can have a profound impact. Encourage patients to share concerns or feelings with family and friends or join a support group to alleviate stress.
8. Check your patient’s feet daily for any cuts, blisters, or signs of infection. Making sure they have proper footwear that is comfortable and well-fitting helps to prevent foot injuries.
By focusing on these aspects, you can help manage diabetes effectively and improve the quality of life for the person you are providing in-home care for.
If you are In need of support and wanting in-home health care services, Eagle Eye Home Care can help. We can ensure your medical care is well managed without needing an expensive healthcare team. Check your availability now.